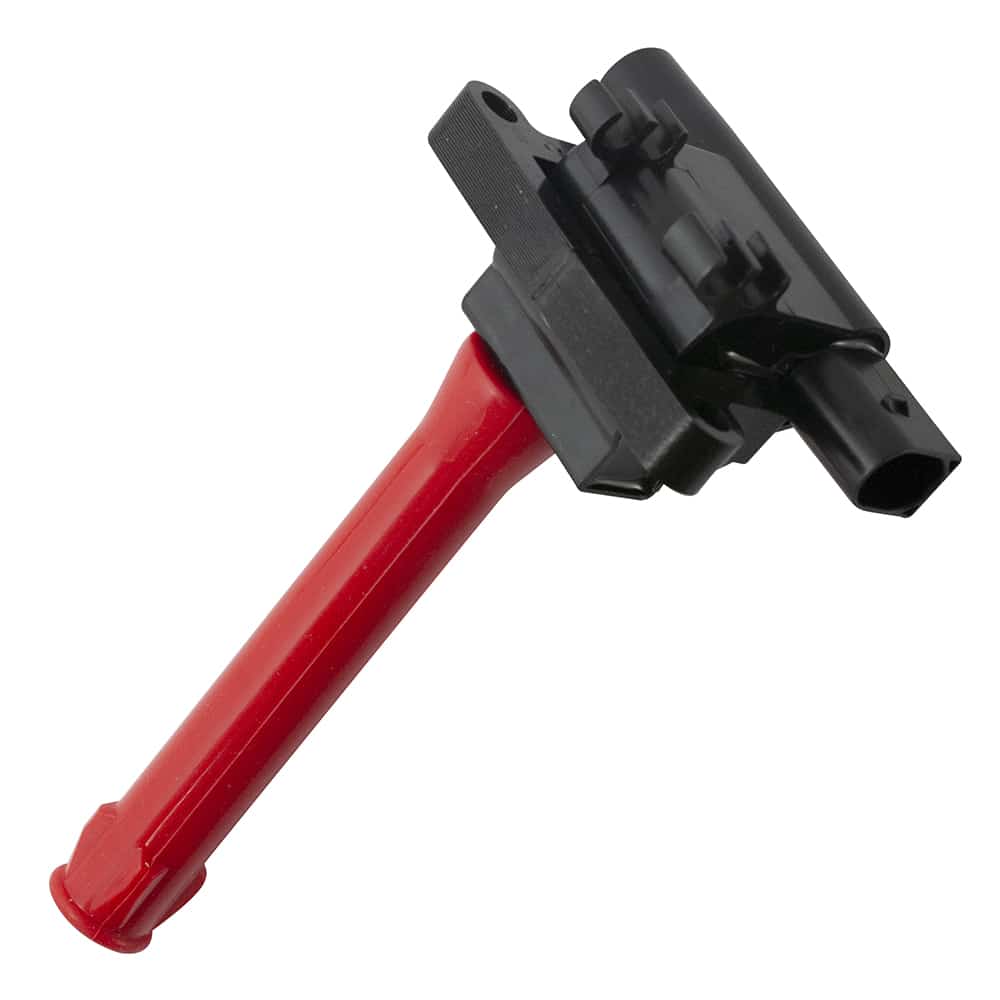
To be operated, internal combustion engines require a system able to ignite the mixture of air and gasoline which is put into the engine and gets compressed inside of its cylinders. This is achieved by an electric spark that is set off in the spark plug, which ignites the mixture, thereby beginning combustion. There are different elements in such systems: a set of coils (monocoils), ignition wires, and DIS-type coils.
Products
We have what you are looking for
-->
Description
Technical data
Composition
Cause of failure
Mounting
Description
STARTING SYSTEMS
To be operated, internal combustion engines require a system able to ignite the mixture of air and gasoline which is put into the engine and gets compressed inside of its cylinders. This is achieved by an electric spark that is set off in the spark plug, which ignites the mixture, thereby beginning combustion. There are different elements in such systems: a set of coils (mono coils), ignition wires, and DIS-type coils.
Types of ignition coils
There are different types of ignition, and each corresponds to a different type of ignition coil:
- Conventional ignition (using a switch)
- Electronic discharge of the ignition capacitator
- Contactless electronic ignition, also known as “transistorised” ignition
- Full electronic ignition. The DIS (direct ignition system) ignition system
What are ignition coils?
The ignition coil is an electromagnetic induction device or inductor, that forms part of an Otto or Wankel cycle alternative internal combustion engine’s ignition. It performs the function of raising the normal on-board voltage (6V, 12V, or 24V, depending on each case) by a value approximately 1,000 times greater to create the electric arc or spark in the spark plug, which allows for ignition of the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
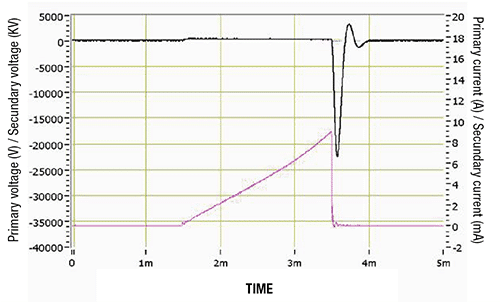
Technical data
The cyclical interruption of the primary is synchronised with the engine, at one rotation in two strokes (2T) or one for every two rotations in four strokes (4T), though there are 4T systems in engines with more than one cylinder, with a spark on each rotation (lost spark system, or DIS).
This interruption was formerly mechanical, performed by the contact breaker or disks, but today it is performed through an electronic circuit, with a power transistor which uses a controller associated with the running of the engine through an engine sensor.

Composition
Operation of ignition coils
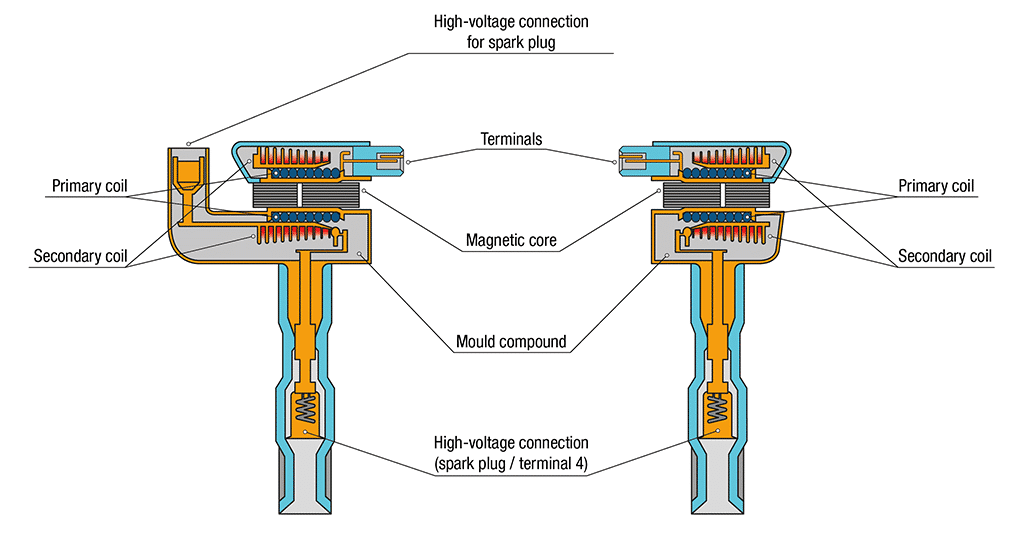
It consists of two winding parts, the primary and secondary, with a loop ratio of approximately 1 to 1,000, with thicknesses inversely proportional to their lengths, and a ferromagnetic core. It is equipped with two connections for the primary, one for positive power from the engine ignition contact, and one for negative power connected to the cyclical interruption device of the primary. The secondary has a ground wire, and another for high voltage output to the spark plug or, where appropriate, to the distributor, and further along, to the engine spark plugs.
Cause of failure
Mounting
Associated documentation
DO YOU WANT MORE INFORMATION?




